Tourism can be seen as being both good and bad for Galapagos. Some of the good parts are that the tourists bring money to the Islands and are a source of income for many Galapagueños. However, there are also bad parts. As more tourists visit the Islands, they will need more places to stay meaning that big hotels could be constructed that possibly endanger nearby wildlife. Let’s explore some of the good bits and bad bits about tourism in Galapagos.
What benefits do tourists bring to the Galapagos Islands?
One of the biggest benefits that tourism brings to the Island is money. Visitors contribute a lot of money to the economy Galapagos Islands. The Islands now generate approximately US$143 million a year through tourism. Additionally, over two thousand people are employed in the tourism industry. Economic migrants come to the Islands from the Ecuadorian mainland seeking jobs and opportunities. Many tour operators and tourists also contribute directly to the Islands, donating to conservation projects across Galapagos. The entrance fees to the National Park (US$100 per adult and US$50 for children in 2014). This tax goes towards supporting a variety of organisations across the archipelago, as can be seen in the diagram below:
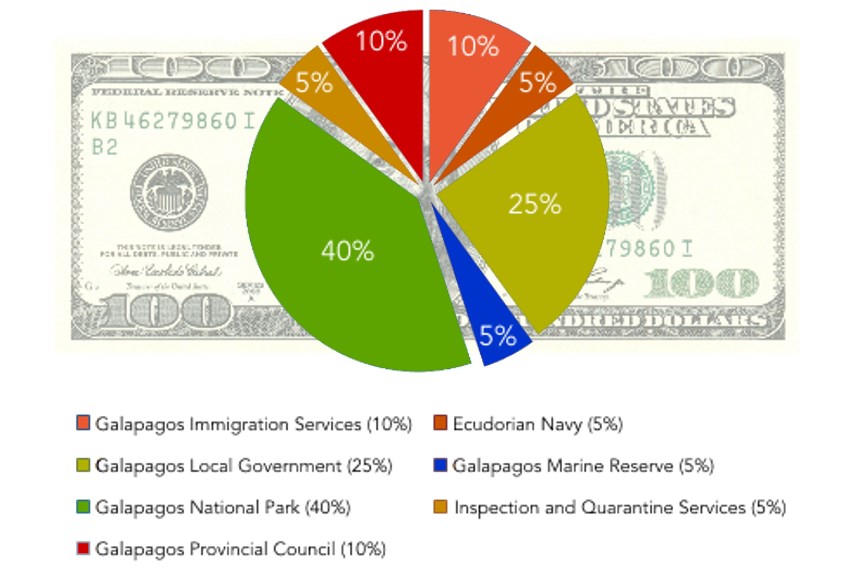
A chart to show how the $100 entrance fee paid by tourists is distributed across the Islands (data from 2011)
What are the negatives to tourism for the Galapagos Islands?
In additions to the positives, tourism also has some negative impacts on Galapagos. When people first started visiting the Islands on holiday, they normally slept and ate on their cruise ships. This meant that any food and provisions needed to come from the mainland rather that the tourists helping the local economy by buying food locally. Now, so many tourists visit the islands that local farmers and fishermen cannot keep up with the requirements of the tourists. This means that food has to be imported from the mainland have to meet demand.
Increased competition amongst hotels has meant that is now cheaper to stay on the Islands than ever before (when compared to staying on a ship). When tourists stay on the Islands, this helps money to go directly to the local community. However, the increasing number of tourists choosing hotels rather than ships has meant that there are growing concerns about the amount of litter being created. As more and more people visit Galapagos, national and international investors could look to build hotels in order to get a share of the lucrative tourism industry. While the National Park areas are protected from development of this kind, the area around these areas has quickly developed with more and more buildings being constructed. Puerto Ayora in particular has seen a rapid growth in the number of cheap hotels, restaurants, souvenir shops and even high rise buildings.
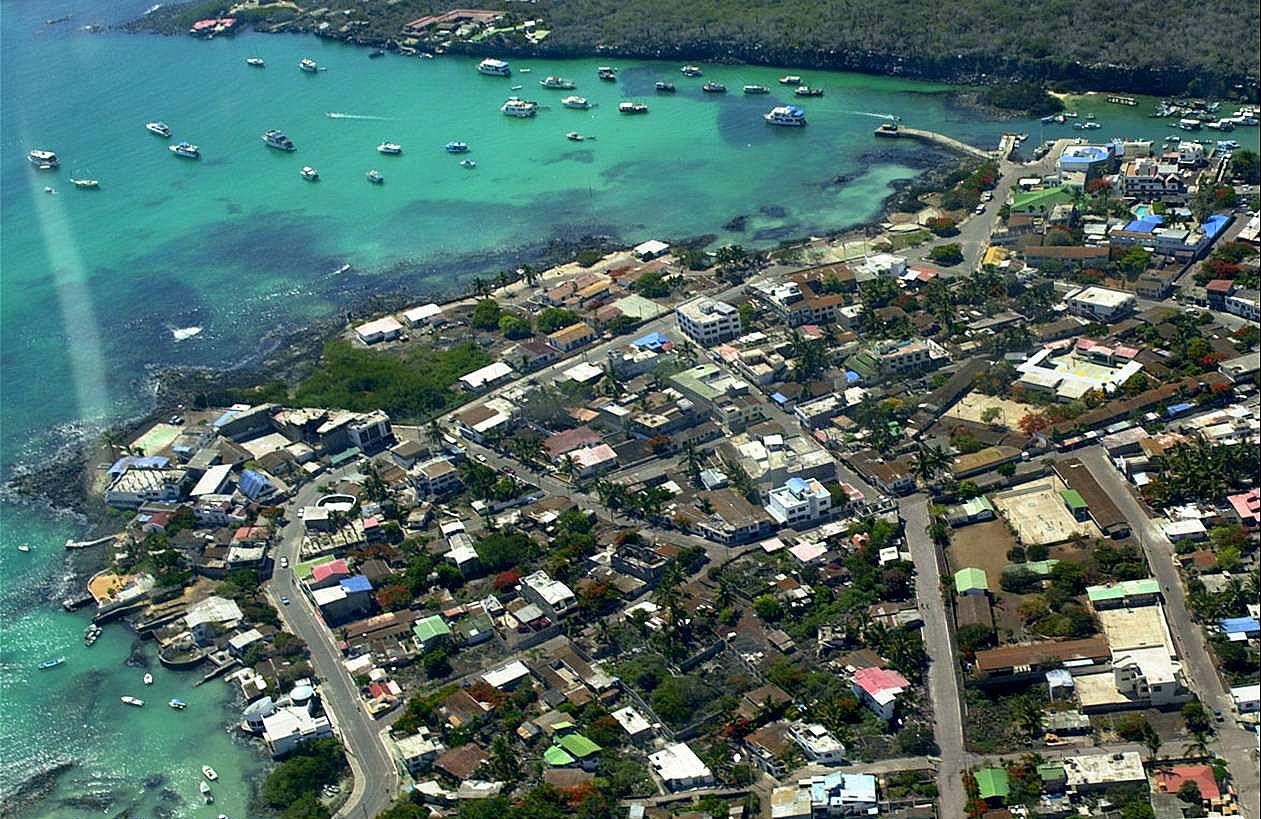

An aerial shot of a rapidly expanding Puerto Ayora, the most populated town on the Islands © Heidi Snell
What do the tourists think?
Since 1990, tourist satisfaction rankings of the wildlife and beauty of the Islands have steadily decreased. More and more, visitors are increasingly saying that they find the Islands surprisingly crowded with tourists. The official guidelines for visitor numbers were set at 12,000 a year in 1968 when the Galapagos Island National Park was first established. However, visitor numbers rose above 12,000 in the 1980s and the limit was raised to 25,000. In 2015, almost ten times as many tourists are now visiting the Islands compared the limit placed over 30 years ago.
Over the years, what tourists want from their holidays has also changed. In recent years, tourists have been more drawn to activity-based holidays. In Galapagos, this demand has seen the rapid development of horseback riding, camping, snorkelling, sport fishing and kayaking activities. However, often little research is done into how such activities may impact on the wildlife. Sadly, not all tourists or tour operators recognise their responsibility to the environment they are visiting.
Poorly maintained ships can contaminate seawater with paint flecks and engine oil. More recently, there have been worries that waste water could be flowing into the ocean and even into drinking water supplies. What impact has tourism had on migration to the Islands? As the popularity of the Islands has grown, so has the number of Ecuadoreans migrating from the mainland to fill the jobs tourism creates. Between 1974 and 1998 the archipelago has seen a 375% increase in population which has had a number of impacts.
Previous: Sustainable Tourism – History of Tourism



